It’s enticing to believe there’s not anything you can do with your refrigerator’s energy prices. Without one, you can not exist, and you can’t turn it off. However, if your fridge has been with you for a long time, through a cut in your energy bill, it could be that a new one would pay for itself in just a few years. And there are always a few improvements that will help you make it as effective as possible, particularly if you have a newer one.
What Is the Refrigerator Energy Efficiency?

How much electricity does a refrigerator use?
If you have a
refrigerator from the 1980s with a top freezer and a size of 19.0-21.4 cubic ft, around 2,000 kWh per year is likely to be used. That implies the aging refrigerator costs you about $.55 a day, $16.67 a month, and $200 a year if you pay $.10 for energy per kWh.
By contrast, a modern-era
Energy Star-rated refrigerator could use just 350 kWh yearly. That’s around $.10 a day, $2.9 a month, and $35 annually at the same $.10 per kWh mark, ensuring you’re aiming at annual savings of $165 by removing the old refrigerator from the equation and in favor of a new one.
If you ever find yourself asking how much electricity does your fridge use, if you calculate your fridge power usage in watts, you can
work that out and your monthly costs. Manufacturers of appliances have been expected to participate in the Energy Guide program since 1980. On any appliance sold in retail shops, the black and yellow tags you see are intended to make it easier for consumers to determine the cost of energy usage before choosing what to purchase.
What is the energy efficiency rating label & Energy star?
The star rating focuses on energy efficiency, which is how competitive a model is compared to other models of the same scale. In contrast to other models of the same scale, more stars are more efficient. Between 1 and 6 stars, the majority of products are given. Technology, however, tends to get better, as does energy conservation. That’s why you’re going to see those super-efficient versions nowadays in stores and online with an extra line for stars since they can have up to 10.
So is 1 star okay?
It is! It just indicates that it’s not as effective on the market as other versions of the same scale, because it’ll cost you more to operate.
You should be sure that you are matching apples-with-apples-and having an educated decision by comparing the star rating on items of the same size or ability. If you use the star rating unintentionally to evaluate products that are not the same size, nevertheless, you might end up making a decision to purchase a product that would cost you more to run and be responsible for more pollution.
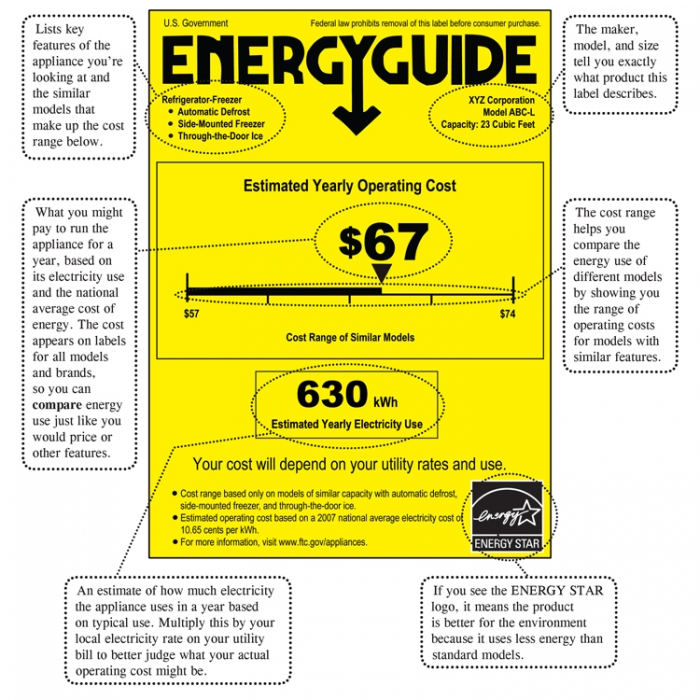
Photo by Penn State
New energy efficiency standards: Auto defrosting, Inverter
Usually, fridges with the freezer on top consume 10 to 25 percent less energy than fridges with the freezer on the bottom or hand. You should also weigh purchasing a refrigerator with an automated ice maker or dispenser on the front to provide the most energy-friendly freezer. Let’s see how energy efficiency standards apply to new refrigerator features: auto defrosting and inverter.
|
Auto Defrosting |
Inverter |
| What does it do? |
In traditional direct cool fridges, the freezer becomes very cold, creating icicles for a period of time. This then calls for the fridge to be manually defrosted. Any of the new models, however, now come with auto-defrost features. |
The traditional refrigerator cycles at a fixed speed on and off, while the inverter refrigerator has the capacity to run at varying speeds. When it restarts, a traditional refrigerator usually creates a noisy noise. At low speed, an inverter refrigerator continues its cycles, thus producing less sound. |
| Is it energy efficient? |
A refrigerator is likely to use about 1 to 2 kilowatt-hours for a whole day (kWh). This translates into an operating expense per fridge of around $150 a year. An auto defrost refrigerator consumes half of an automatic defrost model’s energy but must be periodically defrosted in order to remain energy-efficient. |
The inverter compressor operates more efficiently and at controlled speeds, as compared to a conventional compressor, which means it requires considerably less energy. Refrigerators equipped with digital inverter compressors will approximately consume about 1,800kwh/year, reducing energy usage from around 500 to 380kwh/year. |
| Is it Energy Star approved? |
An Energy Star ranking can be carried by the self-defrosting (auto defrost) and manual defrost freezers. Energy Star quality freezers are at least 10 percent more energy-efficient than the federal minimum requirement. |
Typically, the fridge’s previous compressors had frequency plates consuming 0.6W on standby capacity. As idle, the newest FD-Plus inverter in the market supported by Energy Star compressor further cuts this down to less than 0.1W, the lowest in the refrigerator industry. |
| What are its disadvantages? |
Consider this, annually, one frost-free 15-cubic-foot freezer averaging 12.5 cents per kilowatt-hour would run you about $219, although the comparable manual defrosts freezer costs just around $144 per year. |
To begin with, it has a very slow cooling process, it is one of the major drawbacks to refrigerators with inverters. Unlike standard no-frost refrigerators, they do not freeze automatically and easily. |
How much can you save with a new refrigerator?

In making most homes more effective, significant measures have been taken by appliance manufacturers. The old guidelines are also sound habits, such as having the refrigerator door closed as much as possible and keeping it at the most optimal
temperature setting, but there is plenty to remember.
According to
EnergyStar.gov, you can save up to $1,100 in energy costs over the lifespan of the appliance by getting a new ENERGY STAR certified refrigerator to replace your older model that is over 10 years old.
Are new models of fridges more efficient?
It is definitely true that new fridges are staggeringly more efficient than models manufactured in the 1970s and 80s, up to 75 percent in certain cases. The newly Energy Star specifications stipulate that a 28-cubic-foot fridge should not exceed 403.82 kWh per year- more efficient than any other old refrigerator models.
Overall, refrigerators that can cost hundreds of dollars a year to run, is one of the main drains of your electricity bills. You will save a large amount of money, both instantly and over the lifespan of the new appliance, by substituting an older device for a newer, energy-efficient model.
Tips & Tricks to Use Your Refrigerator as Efficiently as Possible

Now that the environment is shifting and people are planning for a more efficient way of living, many homeowners are starting to look for ways to save money and save electricity without losing any of the conveniences they’re used to at home. That being said, the good news is that it is not only simple and cheap to improve the efficiency of your refrigerator, but it can be achieved in a number of ways.
Replace The Rubber Seal
The Seal prevents your refrigerator from any unnecessary hot air coming in. For gaskets, it is very natural to wear and lose some of their suction when the doors are opened and closed continuously over time. Although your refrigerator will work successfully for years, after just a few years of use, it is inevitable that your gasket will weaken or break. Replacing the seal means more effectively the door to be closed. Thus, preventing the air from escaping out and saving more energy.
Avoid Heat Sources
The compressor strides into high gear when it’s close to heat sources, in order to keep the food cooled to the ideal temperature. This not only forces the refrigerator to work faster, but it is also a fast waste of energy and can also shorten the appliance’s lifetime.
Don’t Use the Ice Makers too Often
Through-the-door ice makers and water dispensers are handy and minimize the need to open the door, so it helps to retain a more steady temperature, yet these efficient devices can increase the energy consumption of your refrigerator by 14 to 20 percent. Mini-doors give you easy access to the most frequently used items. The front door is opened less often and this saves electricity.
Cool the Leftovers
In the next electricity bill, even the slightest specifics will save you a great deal of cash. By providing time for your leftovers to cool down after a meal, you reduce the amount of heat applied to your appliance’s interior. Before putting your
dish in the refrigerator, you can also store your food properly in safe packaging or Plastic tubs, as it stops any residual heat from leaking through your unit.
Don’t Open the Fridge When not Necessary
No matter what kind of refrigerator you have, this is the most simple option to minimize your energy consumption. Standing in front of an open fridge will have a big effect on the energy bill. It takes more energy to restore it to its expected temperature when the cool air escapes from your appliance. Decide what you want before opening the doors of your refrigerator or freezer if possible.
Decrease Ice Accumulation
Depending on your fridge, manual defrosting can be needed. Accumulation can collect inside the refrigerator on the coils, causing the machine to work overtime. It will be impossible for the fridge to sustain colder temperatures if you do not routinely defrost the refrigerator and freezer.
Initiate (if Applicable) Your Power Saving Switch
While not all refrigerators are fitted with this function, many new appliances now have portable heaters installed into the walls to prevent condensing moisture on the outside surface. You should activate the energy-saver or power-saver switch to quickly uninstall this function until you have a great deal of visible condensation on your device.
Today’s fridges consume much less electricity than older ones, due to new advancements in insulation and compressors. You can optimize your energy and dollar savings with an Energy Star certified refrigerator without losing the specifications you want. So, choose to save your money while conserving the environment by reducing your electricity footprint.
Read more about Best Energy-Efficient Refrigerators From Consumer Reports’ Tests




